Blue Forest Petrified Wood: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Blue Forest Petrified Wood?
Blue Forest Petrified Wood is a unique type of fossilized wood found in the Blue Forest area of the Green River Formation in southwestern Wyoming, USA. This petrified wood is renowned for its stunning blue and green hues, which result from the mineralization process involving silica and other trace minerals.
Importance and Relevance in Geology and Paleontology
Blue Forest Petrified Wood holds significant value in both geology and paleontology. It provides insights into ancient ecosystems, climatic conditions, and the process of fossilization. Its aesthetic appeal and rarity also make it a valuable collector’s item and a subject of scientific interest.
Geological Background: Blue Forest Petrified Wood
Formation Process of Blue Forest Petrified Wood
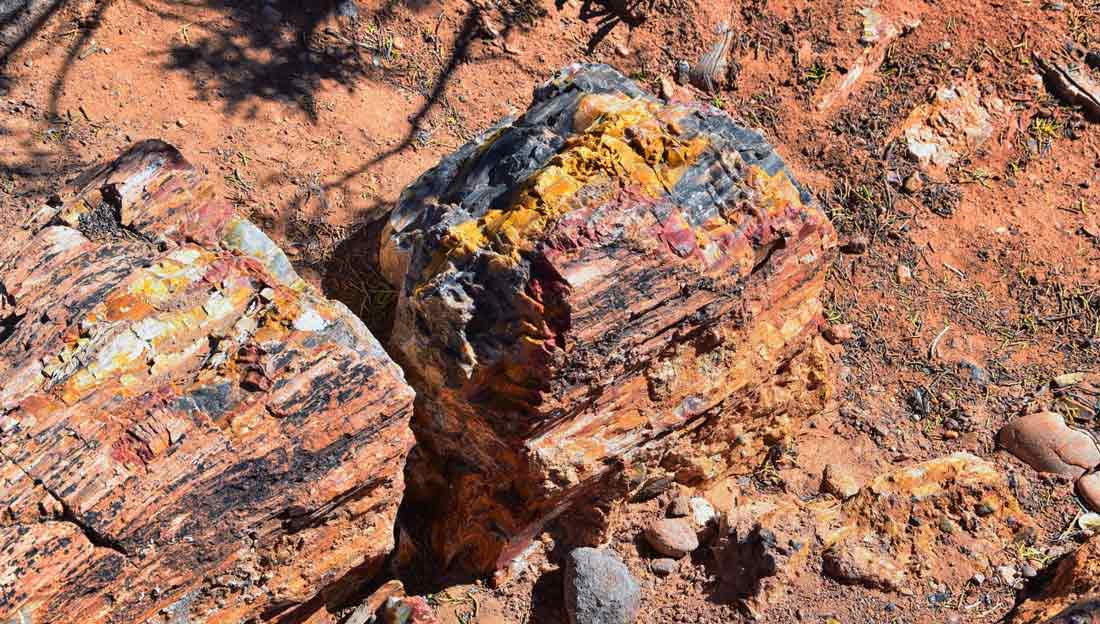
Petrified wood forms through a process called permineralization, where organic material is gradually replaced by minerals. This occurs when wood is buried under sediment and exposed to mineral-rich water. Over millions of years, the minerals crystallize within the wood’s cellular structure, preserving its shape and texture.

Specific Conditions Required for Blue Forest Petrified Wood Formation
The unique blue and green colors of Petrified Wood are the result of specific geological conditions. Silica-rich waters, along with trace elements like iron and copper, contribute to the distinctive coloration. These conditions were prevalent in the ancient lake environments of the Green River Formation during the Eocene epoch.
Geological Era of Origin
Blue Forest Petrified Wood dates back to the Eocene epoch, approximately 56 to 33.9 million years ago. This period was characterized by a warm climate and diverse ecosystems, which are reflected in the fossilized remains found in the region.
Location and Discovery: Blue Forest Petrified Wood
The Blue Forest is located within the Green River Formation in southwestern Wyoming, primarily in Sweetwater County. This area is renowned for its rich deposits of fossilized plants, fish, and other ancient life forms.
The discovery of Petrified Wood dates back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Early explorers and geologists were captivated by the vibrant colors and well-preserved structures of the petrified wood, leading to numerous scientific expeditions and studies.
Over the years, various expeditions have contributed to our understanding of Blue Forest Petrified Wood. Notable research conducted by institutions like the University of Wyoming and the Smithsonian Institution has helped uncover the geological history and significance of these fossils.
Characteristics and Appearance: Blue Forest Petrified Wood
Blue Forest Petrified Wood is characterized by its vivid blue, green, and turquoise hues. These colors result from the presence of minerals like silica, iron, and copper, which permeate the wood during fossilization. The wood retains its original structure, with tree rings and grain patterns clearly visible.
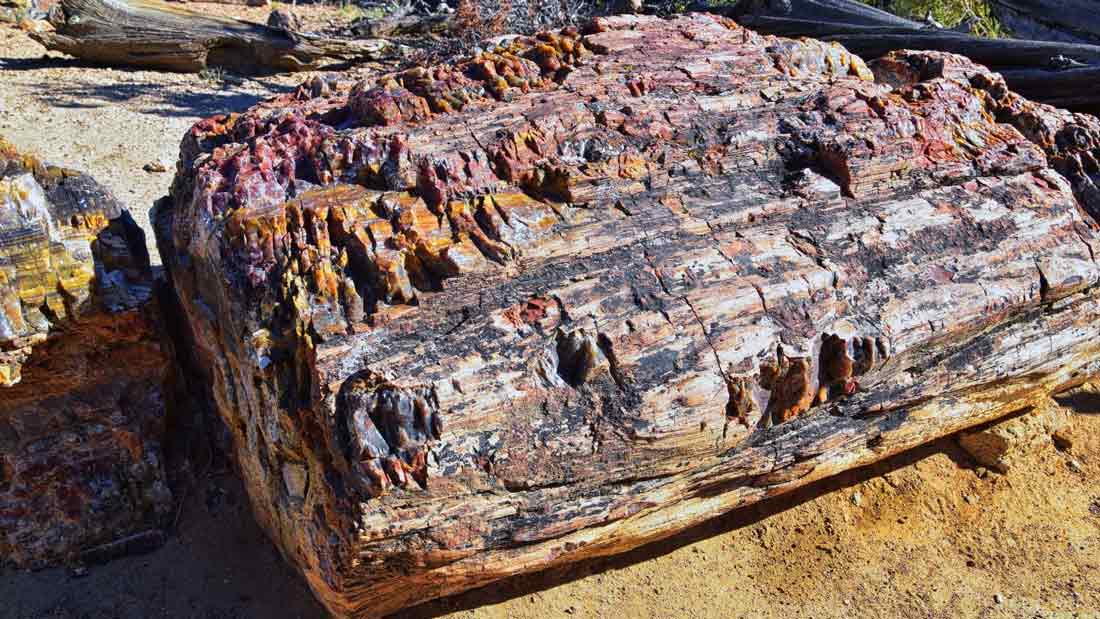

The color variations in Blue Forest Petrified Wood can range from deep blue to light green, often with intricate patterns and swirls. These patterns are a result of the different mineral compositions and the conditions under which the wood fossilized.
The primary mineral component of Petrified Wood is silica, which gives it a hardness of about 7 on the Mohs scale. This makes it relatively durable and suitable for various applications, including jewelry and decorative items.
Scientific Significance
Importance in Understanding Ancient Ecosystems
Blue Forest Petrified Wood provides valuable information about ancient ecosystems, particularly the types of trees and vegetation that existed during the Eocene epoch. By studying these fossils, scientists can infer the climatic conditions and environmental factors of that time.
Contributions to the Study of Paleobotany
Paleobotany, the study of ancient plants, greatly benefits from the examination of Petrified Wood. These fossils offer a detailed record of plant life from millions of years ago, helping researchers understand plant evolution and diversity.
Insights into Climatic Conditions of the Past

The mineral content and preservation of Blue Forest Petrified Wood offer clues about the climatic conditions of the Eocene epoch. By analyzing the chemical composition of these fossils, scientists can reconstruct past climates and better understand how they have changed over time.
Types and Classifications
Blue Forest Petrified Wood can be classified into several types based on mineral content and coloration. Some specimens exhibit vibrant blue hues, while others may have more green or turquoise tones. The variety of colors and patterns is a testament to the diverse geological conditions that existed in the area.
The classification of Blue Forest Petrified Wood also considers the specific minerals present in the fossil. Common minerals include quartz, chalcedony, and opal, each contributing to the unique appearance of the wood. Trace elements like iron and copper further influence the coloration.
The fossilization process of Petrified Wood can vary, leading to different textures and degrees of preservation. Some specimens may be completely mineralized, while others retain portions of the original organic material. These variations provide valuable insights into the fossilization process.
Uses and Applications
Use in Jewelry and Decoration

Due to its striking colors and patterns, Blue Forest Petrified Wood is highly sought after for use in jewelry and decorative items. Its durability and unique appearance make it an excellent choice for creating eye-catching pieces.
Educational and Research Applications
Petrified Wood is also valuable for educational and research purposes. It is used in museums, universities, and other institutions to teach about ancient ecosystems, fossilization processes, and geological history.
Commercial Value and Trade
The commercial value of Petrified Wood can be significant, particularly for high-quality specimens. It is traded among collectors, jewelers, and enthusiasts, contributing to the economic importance of this fossil resource.
Collection and Preservation
Collecting Blue Forest Petrified Wood requires careful consideration of ethical and legal guidelines. It is important to respect the natural environment and obtain specimens through legal means to avoid damaging the site and depleting resources.
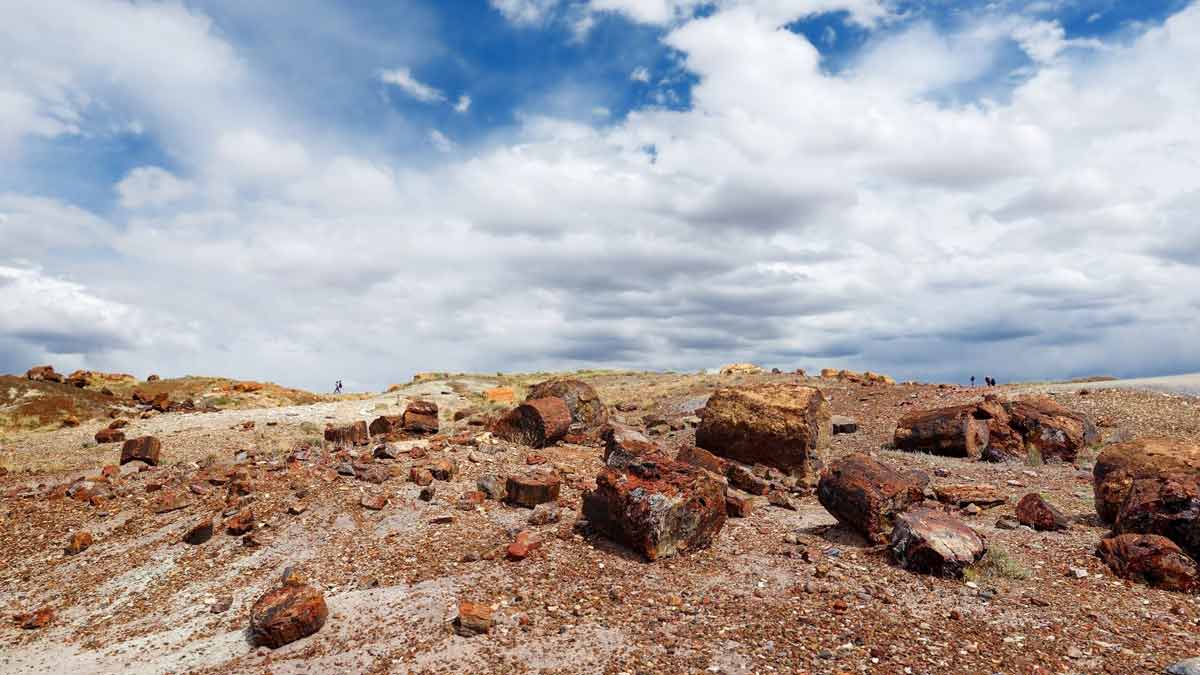

Preserving and displaying Blue Forest Petrified Wood involves protecting it from environmental factors like moisture and temperature fluctuations. Proper cleaning, storage, and display techniques help maintain the integrity and appearance of the fossils.
There are legal regulations in place to protect petrified wood sites, including restrictions on collecting and exporting fossils. These regulations aim to preserve the natural heritage and ensure that these valuable resources remain available for future generations.
Famous Specimens and Exhibits
Several notable specimens of Blue Forest Petrified Wood are housed in museums and private collections worldwide. These specimens are often showcased for their exceptional color, size, and preservation, providing valuable educational and research opportunities.
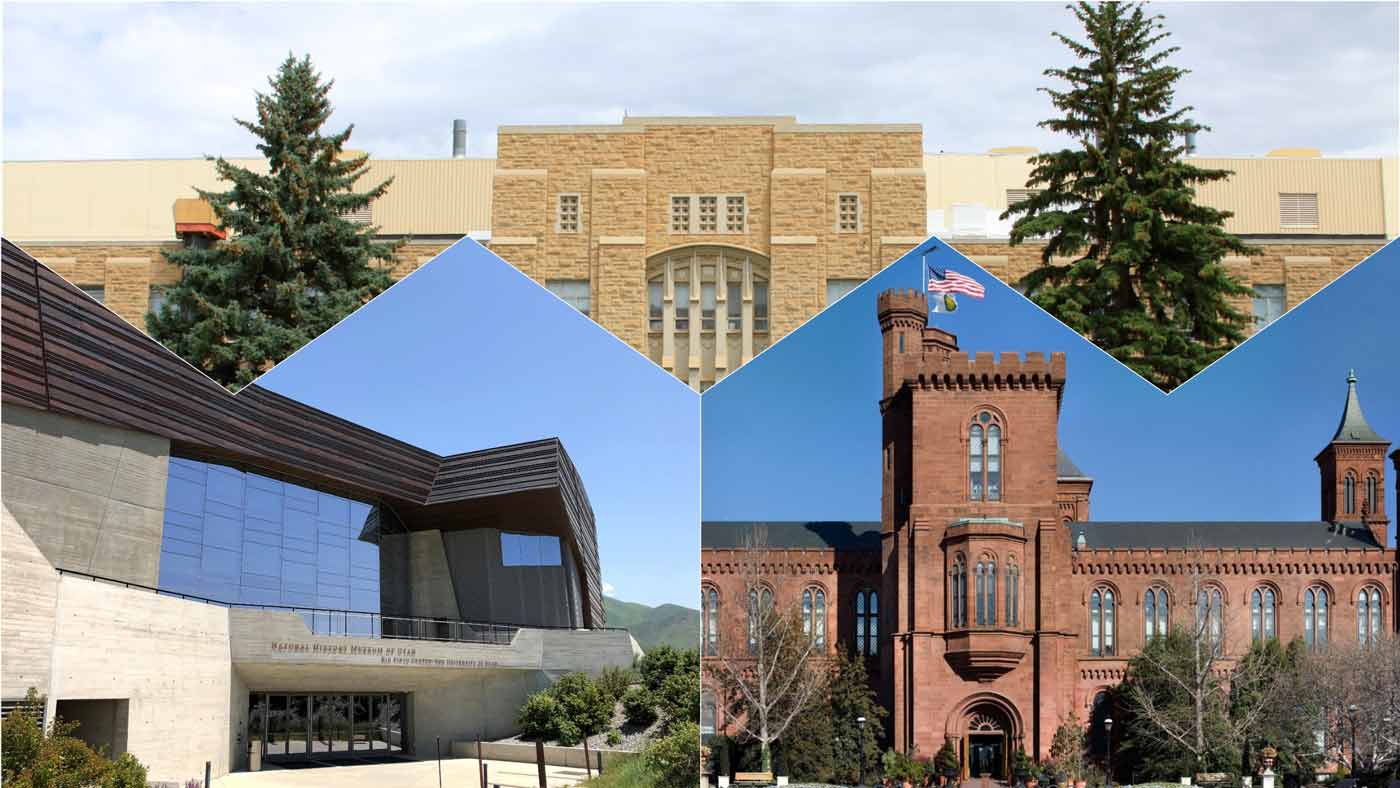

Major exhibitions featuring Blue Forest Petrified Wood include those at the Smithsonian Institution, the Natural History Museum of Utah, and the University of Wyoming. These exhibitions highlight the scientific and aesthetic significance of these fossils.
Exhibiting Blue Forest Petrified Wood in museums and educational institutions plays a crucial role in public education. These displays help raise awareness about ancient ecosystems, fossilization processes, and the importance of geological conservation.
Challenges and Conservation
Blue Forest Petrified Wood sites face several threats, including illegal collecting, environmental degradation, and climate change. These factors can lead to the loss of valuable fossils and the destruction of the natural landscape.
Conservation efforts aim to protect Blue Forest Petrified Wood sites through legal regulations, public awareness campaigns, and scientific research. Organizations like the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) and local conservation groups play a key role in these initiatives.

Local and global organizations work together to preserve Blue Forest Petrified Wood sites. These collaborations involve monitoring, research, and educational programs that promote the sustainable use and conservation of these valuable resources.
Personal Stories and Case Studies
Accounts from Geologists and Paleontologists
Geologists and paleontologists share fascinating accounts of their discoveries and research involving Blue Forest Petrified Wood. These stories provide insights into the challenges and rewards of studying these ancient fossils.
Stories of Notable Discoveries
There are numerous stories of notable discoveries of Blue Forest Petrified Wood, often involving serendipitous finds and dedicated fieldwork. These discoveries have significantly advanced our understanding of ancient ecosystems and fossilization processes.
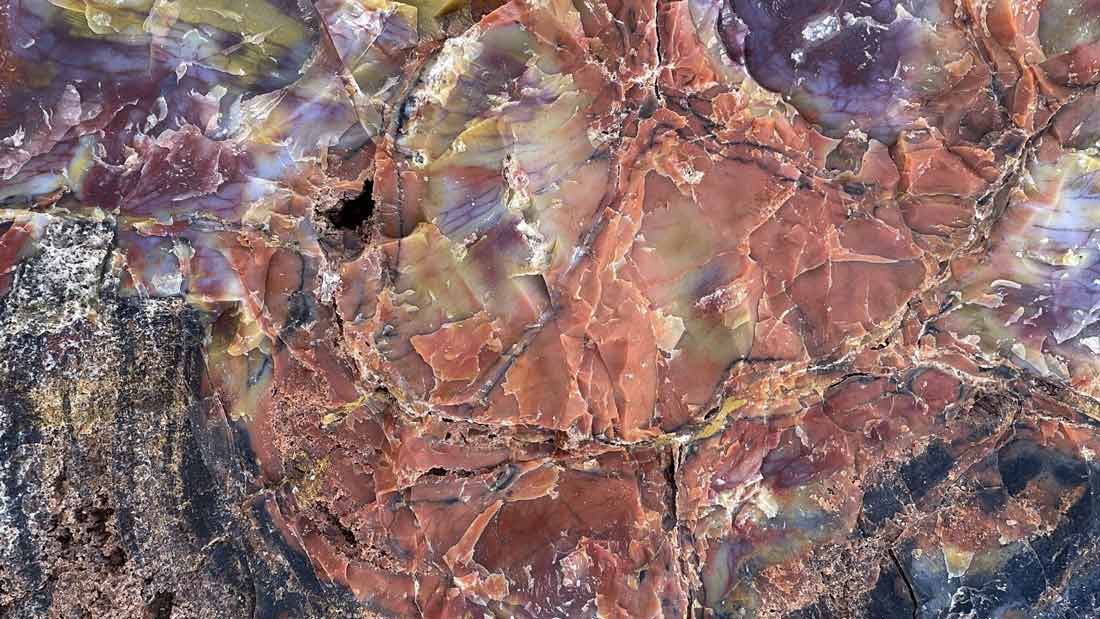

Impact on Local Communities and Tourism
The presence of Blue Forest Petrified Wood has a positive impact on local communities, particularly through tourism. Visitors are drawn to the unique fossils, boosting local economies and raising awareness about geological conservation.
Expert Insights
Leading experts in geology and paleontology provide valuable insights into the significance of Blue Forest Petrified Wood. Their quotes and perspectives highlight the ongoing research and discoveries in this field.
Recent research on Blue Forest Petrified Wood continues to uncover new information about its formation, mineral composition, and the ancient environments in which it formed. These findings contribute to the broader understanding of Earth’s geological history.
Future research on Blue Forest Petrified Wood will likely focus on advanced analytical techniques, such as isotopic analysis and micro-imaging, to further unravel the complexities of fossilization and ancient ecosystems.
Conclusion
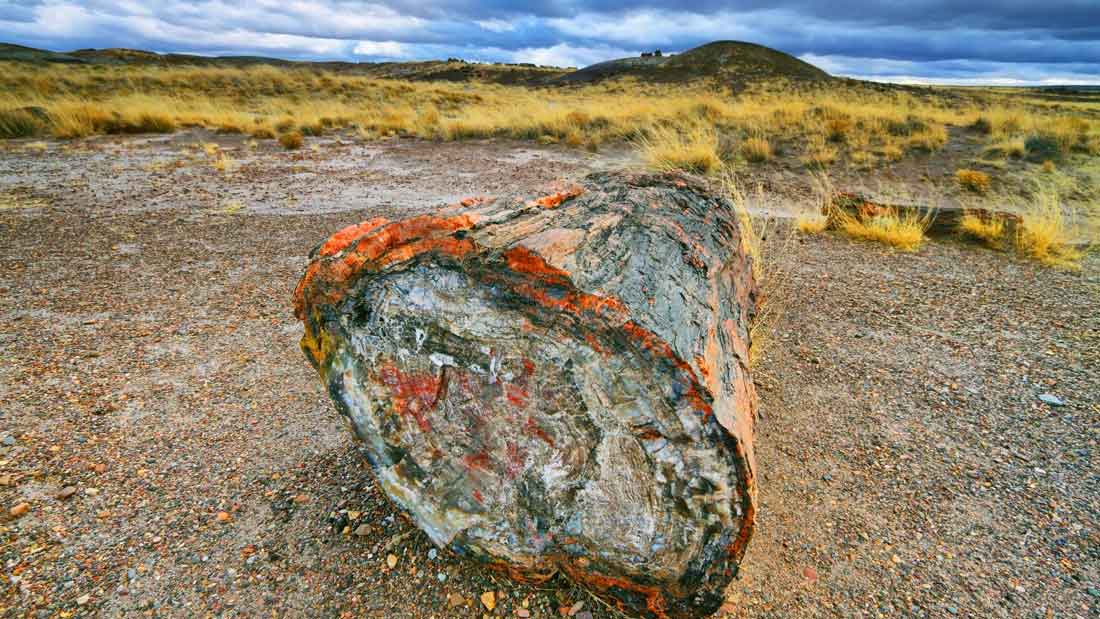

Blue Forest Petrified Wood is a remarkable fossil resource that provides valuable insights into ancient ecosystems, climatic conditions, and the process of fossilization. Its unique appearance and scientific significance make it an important subject of study and conservation.
To ensure the preservation of Blue Forest Petrified Wood, it is essential to support conservation efforts, adhere to ethical collecting practices, and promote public education. By doing so, we can safeguard these valuable fossils for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Blue Forest Petrified Wood is a unique type of fossilized wood found in Wyoming, USA. It’s known for its vibrant blue and green hues due to minerals replacing the organic material.
It holds geological and paleontological significance. It reveals details about ancient ecosystems, climatic conditions, and the fossilization process. It’s also valuable for collectors and scientific study.
Through a process called permineralization. Wood gets buried and exposed to mineral-rich water over millions of years, slowly replacing the organic material with minerals.
Silica-rich water with trace elements like iron and copper during fossilization contribute to the unique coloration.
Blue Forest Petrified Wood displays vivid blue, green, and turquoise hues. It retains the original wood structure with visible tree rings and grain patterns.
It provides information about ancient plant life, ecosystems, and climatic conditions of the Eocene epoch. It contributes to the study of paleobotany and helps reconstruct past climates.
Due to its beauty, it’s used in jewelry and decorative items. It also has educational and research applications in museums and universities. High-quality specimens can hold commercial value.
Collecting regulations exist. It’s crucial to respect the environment and obtain specimens through legal means to avoid harming the site or depleting resources.
Protect it from moisture and temperature fluctuations. Proper cleaning, storage, and display techniques are essential for maintaining its integrity.
Illegal collecting, environmental degradation, and climate change threaten these sites.
Supporting conservation efforts, adhering to ethical collecting practices, and promoting public education are crucial. Organizations like the BLM play a key role.
Museums and collections worldwide showcase notable specimens. Exhibitions at the Smithsonian Institution and other institutions highlight their significance.
Ongoing research explores the formation, mineral composition, and the ancient environments using advanced techniques, providing new insights.
Advanced analytical techniques like isotopic analysis and micro-imaging are expected to be used to further understand fossilization and ancient ecosystems.